The author of the article
Boris Lipovetskiy, DMD, 31 years experience
In this guide, we have provided detailed instructions on what to do if you are experiencing a toothache. Our specialists have compiled descriptions of various types of tooth pain – from minor sensitivity to severe conditions. They will discuss possible causes, including cavities, gum recession, and pulpitis.
We will help you understand the causes and symptoms of toothache, as well as the importance of professional diagnosis and treatment in a dental office. Whether you are looking for immediate relief or long-term results, our doctors have gathered practical advice for addressing the root cause of toothache.

The author of the article is Dr. Boris Lipovetskiy, a dentist with over 30 years of experience. He is the founder of the Advanced Dental Wellness Center and the author of the «Guide to Treating Toothache».
Article Contents:
- Types of Toothache
- Causes of Toothache
- When Should I See a Doctor and What Does Treatment Involve?
- How Can I Prevent a Toothache?
Schedule a consultation at our dental office in Fort Lauderdale! We'll address your toothache and its root cause!
What is Toothache?
Toothache is pain that occurs in a tooth or in the gum tissues around it. According to the study "Managing Tooth Pain in General Practice" published by PMC – NCBI, toothache usually results from cavities, infection, or injury. The pain in a tooth can range from mild to very severe and can be constant or intermittent. Often, it intensifies under the influence of irritants (hot/cold, sweet/salty/sour, as well as while chewing or biting).
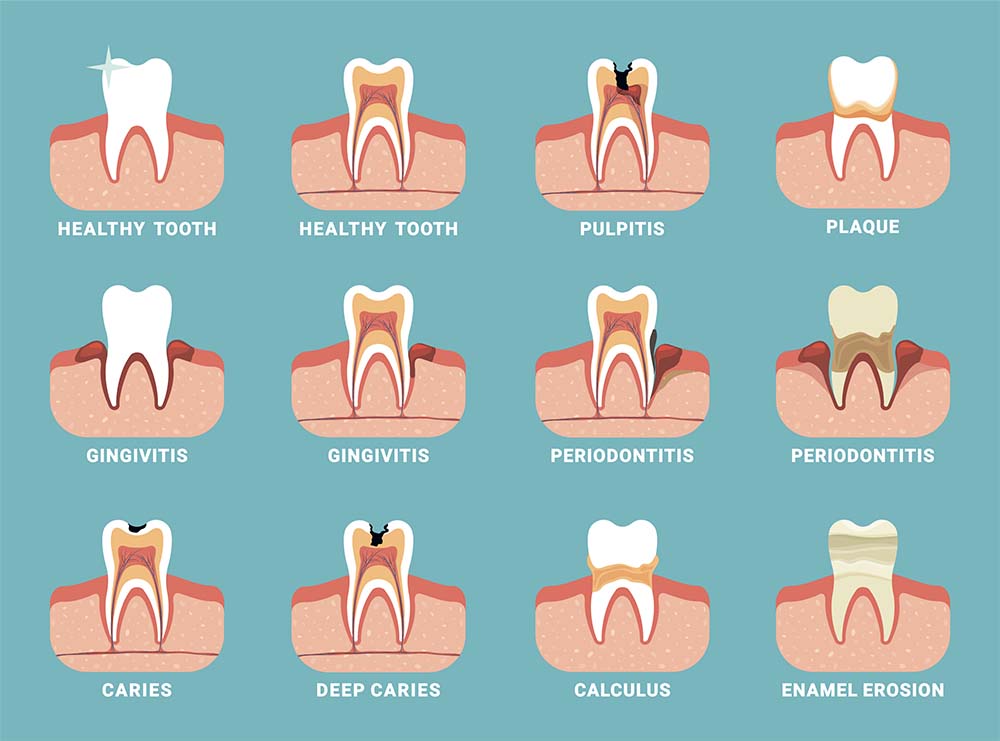
To prevent complications, it is recommended to consult a dentist – only a professional can provide an accurate diagnosis.
Types of Toothache
Dentists emphasize that each case is unique. Therefore, a comprehensive diagnosis is required to understand the real cause of the pain and to eliminate its source without complications.
General toothache is usually caused by factors such as cavities, gum disease, tooth abscess, or a damaged filling. It can also be a symptom of teeth grinding or infection.
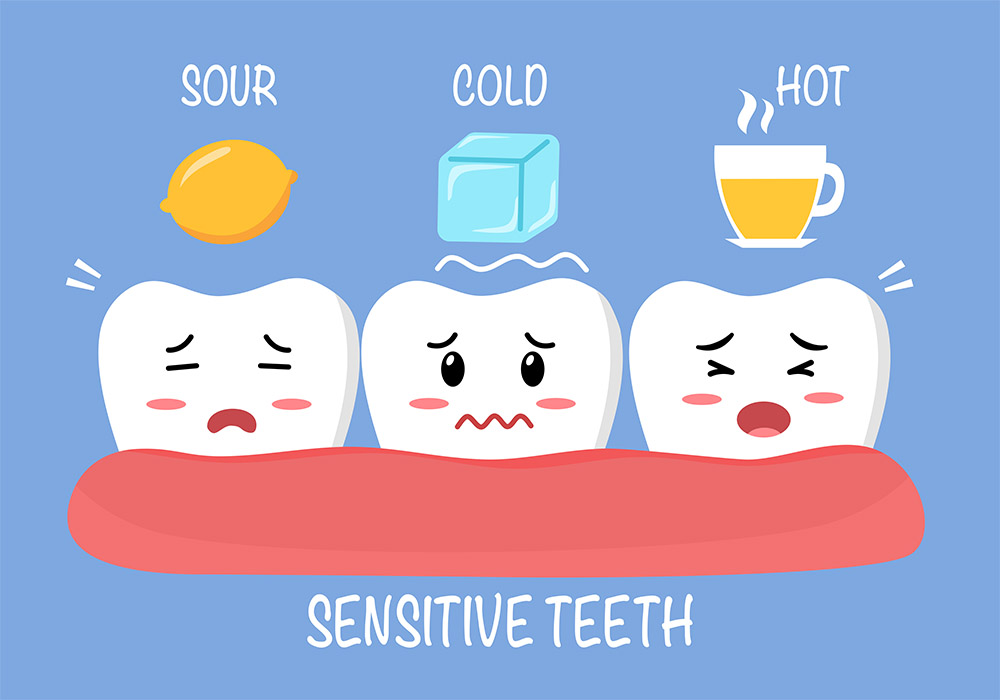
Patients often feel it as a dull or throbbing pain. General toothache is also characterized by:
-
Increased Sensitivity – temporary discomfort when in contact with cold or hot. This is observed with exposed tooth roots, early-stage cavities, and enamel thinning.
-
Aching, Short-term – sensitivity intensifies when the tooth is exposed to acids or sweet substances. Painful reaction when biting hard foods. This signals the development of moderate cavities or periodontitis.
-
Long-lasting, throbbing pain becomes more intense due to the infection's proximity to the nerve. The pressure caused by inflammation of the tooth's internal tissues gives it a throbbing character. Indicates deep cavities.
-
Sharp Pain – acute, piercing pain, often associated with pulpitis (nerve inflammation). Pain sensations can spread throughout the jaw, radiating to the ear. Intensifies at night, when chewing on the affected tooth. Shooting pain also occurs with injuries.
-
Dull, Constant Pain – that intensifies when pressing on the affected tooth or gum. Maybe a sign of periodontitis.
-
Jaw Pain Near the Ears – intensifies with various movements, such as opening the mouth, chewing, speaking, and yawning. It may indicate TMJ (temporomandibular joint) disorders. Additionally, wisdom teeth eruption can cause severe pain. The gums become inflamed, and the pain radiates to adjacent teeth, especially if they erupt abnormally.

Seek Immediate Dental Care for a Toothache
Boris Lipovetskiy
Dentist with 30 years of experience
Delaying treatment can lead to more serious dental problems. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene are key to preventing and treating general tooth pain.
According to a study by the University of Washington School of Dentistry, impacted wisdom teeth can cause pain, swelling, or gum problems. This occurs when the third molars erupt and become trapped or misaligned. This can lead to pain, swelling, and sometimes infection.
Wisdom toothache is often described as a deep, aching sensation in the back of the mouth. It can radiate to the jaw and ear. In cases of complications, swelling or difficulty opening the mouth may be observed.
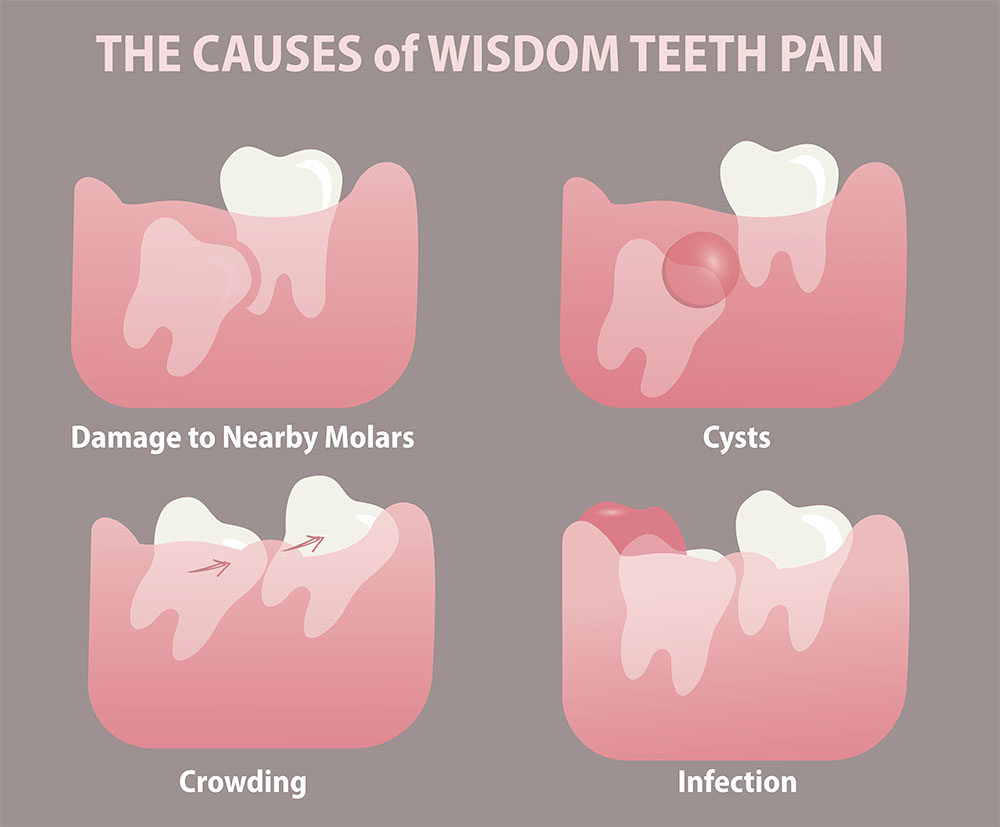
A dental examination, including X-rays, is necessary to assess the position and health of wisdom teeth. In cases of impaction or misalignment, extraction is often recommended. Ignoring wisdom toothache can lead to complications such as infections or cysts.
Answers to Questions
Teeth are highly sensitive structures. They consist of a hard outer enamel layer, an underlying layer of dentin, and a central pulp. The pulp contains nerve fibers and blood vessels, making it hypersensitive.
Causes of Toothache
-
Cavities – the most common cause. Tooth enamel is destroyed by acids produced by bacteria. Researchers at Harvard Medical School discuss how tooth pain intensifies from cold due to damage from cavities or gum erosion.
-
Chips, Cracks, Gum Recession – contribute to increased tooth sensitivity. The sensitive part of the tooth, the dentin, becomes exposed. Exposed tooth neck affects its reaction to cold, hot, sweet, and sour.
-
Pulpitis – bacteria penetrate through damaged enamel, reaching the tooth pulp. It becomes inflamed, causing acute pain. Impacts, falls, or other injuries can also damage the tooth, leading to inflammation.
-
Periodontitis – bacteria from dental plaque and carious cavities penetrate the gum and bone tissue around the tooth. Resulting in severe pain and tooth mobility.
-
Abscess – a collection of pus at the tooth root, formed in response to infection. Can lead to tissue swelling, high body temperature, chills, general weakness. Causes sharp, throbbing pain.
-
Wisdom Tooth Eruption – its sharp edge can irritate the surrounding soft tissues, causing pain. They may emerge at an incorrect angle or direction due to limited space, exerting forced pressure on adjacent teeth.
-
Gum Inflammation – can arise from inadequate oral hygiene. Hardened dental plaque irritates soft tissues, provoking pain. Roughness of teeth, fillings, or orthodontic appliances can also irritate gums, causing pain, sensitivity, and bleeding.
-
TMJ Dysfunction – dysfunction of the jaw joints is accompanied by pain in the face, neck, ears. Caused by involuntary teeth clenching/bruxism, excessive chewing, tense facial muscles, and improper bite.
-
Dental Errors – can be a source of toothache and discomfort for the patient.
- A filling that doesn't fit properly, creating a gap – a breeding ground for bacteria.
- A filling that is higher than the bite level – causes pressure on adjacent teeth during chewing.
- Incorrect shape of a crown or bridge puts pressure on surrounding teeth, gums, or jaw joints.
- Failure to completely remove affected tissues during tooth preparation for a crown or bridge, leading to the development of cavities.

When Teeth are Not the Culprit: Unobvious Sources
Boris Lipovetskiy
Dentist with 30 years of experience
According to research Odontogenic Sinusitis can be associated with tooth pain. ENT diseases (sinusitis, rhinosinusitis, ear diseases) can manifest symptoms similar to toothache. A doctor's consultation is necessary. Only after a thorough examination can the doctor identify the source of the pain, suggest appropriate treatment, or refer to a specialist.
The variety of causes of a toothache highlight the importance of diagnosis. Early diagnosis will allow us to accurately determine the root of the problem and develop a treatment plan for the actual cause of the pain.
Answers to Questions
The duration depends on its cause. In cases of cavities or nerve irritation, acute pain can last from a few minutes to several hours. Chronic pain due to cavities or gum inflammation can persist for several days or weeks, occurring intermittently. After tooth extraction or cavity treatment, pain can last for several days, gradually decreasing as healing progresses.
How Is Toothache Treated?
Only a qualified dentist can accurately diagnose and provide proper treatment. Do not attempt to self-medicate. The treatment of toothache in a clinic depends on the diagnosis and the cause of the pain. It includes the following stages:
The dentist conducts a detailed examination and collects a medical history to identify pain symptoms. The patient describes the nature of the pain, the time of its onset, and factors that influence its intensification or alleviation.
The dentist may order X-rays for a more detailed study of the condition of the teeth and roots. Additional sensitivity tests may be conducted. Based on the examination results, the dentist determines the cause of the toothache and develops a treatment plan, which includes methods to eliminate the cause of the pain and restore the tooth.
- For cavities: Removal of decayed tissues and filling the tooth to restore its structure.
- For pulpitis: Root canal treatment, removal of the inflamed part of the pulp.
- For gum inflammation: Procedures to improve the health of the gums and periodontium, including cleaning of periodontal pockets.
- For an abscess: Drainage procedure to remove pus.
- For TMJ dysfunction: Physiotherapy, prescribing exercises for muscle relaxation, and wearing occlusal splints.
The dentist provides advice on dental care. Prescribes medication to alleviate pain, prevent infection, and accelerate the healing process. A follow-up appointment may be scheduled, if necessary, to adjust the treatment plan.
When is it necessary to remove a painful tooth? A tooth is removed if it has sustained severe trauma or extensive damage that cannot be restored. Also, if wisdom teeth are causing problems, their removal is often recommended.
In a holistic approach, we use ozonated water for rinsing cavities or after the extraction of dead teeth. For deep caries, we use ozone gas and laser treatment to remove the carious tissue (disinfection). We also employ laser therapy for treating the soft tissues of the gums in cases of periodontal pockets.
I invite everyone who is looking for an optimal way to holistic treat teeth to a consultation! We will develop a restoration plan based on holistic principles.
Pain relief is a temporary way to alleviate discomfort until you visit a dentist to diagnose and treat the underlying cause.

Methods to Alleviate Toothache:
-
Over-the-counter Analgesics: For example, acetaminophen. It acts on the central nervous system, blocking pain signals in the brain.
-
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Such as aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen. They reduce the production of prostaglandins, substances involved in inflammatory processes.
When using any pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs, it's important to adhere to the recommended dosages. Exceeding them can cause side effects.
Answers to Questions
Unbearable tooth pain is a clear signal of a significant problem. Don't wait for relief at home; seek urgent medical attention.
Methods that can help alleviate tooth pain at home:
-
Taking over-the-counter pain relievers / anti-inflammatory drugs
-
Applying cold to the area of the problematic tooth
-
Rinsing the mouth with a saline solution (1 teaspoon per cup of warm water) or diluted hydrogen peroxide (1:1)
-
Eating soft and warm food/drinks. Avoid chewing on the side where the tooth hurts
-
Gently massaging the earlobes and the area between the thumb and index finger on the hand
-
Using toothpaste for sensitive teeth
These methods only provide temporary relief. To determine the underlying cause of toothache, a visit to the dentist is necessary.
After diagnosis, the dentist may prescribe therapeutic treatment – various procedures and measures to alleviate pain and restore oral health. They may also prescribe medications for home use and provide recommendations.
This is especially true for antibiotics. Self-medication without consultation is not recommended. Incorrect use or dosage can lead to side effects. Only a doctor can select the appropriate drugs, taking into account the patient's characteristics and the nature of the illness.
Prevention of Tooth Pain
What can be done to prevent toothache?
-
Brush your teeth twice a day using a toothbrush with soft bristles
-
Clean between your teeth daily using dental floss
-
Limit the consumption of sugary confectionery
-
Visit the dentist twice a year for preventive check-ups and professional teeth cleaning
-
Use mouthwashes with antiseptic properties to reduce bacteria
-
Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption – both can deteriorate the condition of teeth/gums
-
Wear protective gear during active sports to prevent dental injuries
-
Manage stress levels – it affects oral health. Practice relaxation techniques to manage stress
-
Seek immediate dental care at the first signs of pain
Following these recommendations can help create a healthy environment in the oral cavity and prevent pain.
Q&A
Yes, toothache is often related to the condition of the gums. For example, in periodontitis (inflammation of the gums and surrounding tissues), sensitivity and pain when pressing on the gum can occur. Dental plaque and tartar lead to their inflammation and pain. Or, during the eruption of wisdom teeth, gum inflammation can occur, accompanied by pain and discomfort. Injuries caused by brushing teeth or careless use of dental floss can also cause gum disease.
Sources of information
- Toothache – Dr. A.O. Awotile department of restorative dentistry. Dental center, Lasuth
- Diagnosis and treatment of abnormal dental pain – Department of oral health and clinical science, Tokyo dental college, Tokyo, Japan
- Management of dental pain in primary care – Melbourne dental school, University of Melbourne
- Oral Diagnosis Diagnosing the Patient in Pain – JK Mitchell, DDS, MEd
- Dental pain: Dentine sensitivity, hypersensitivity and cracked tooth syndrome


