The author of the article
Boris Lipovetskiy, DMD, 31 years experience
Experiencing sharp pain while eating? Do your teeth react to cold, hot, or acidic substances? Do they even hurt when inhaling cold air or during brushing? All these are signs of increased dental sensitivity, a problem that can intensify over time. How can you prevent it from getting worse?
If you experience such symptoms, visit Advanced Dental office in Fort Lauderdale.
Tooth hypersensitivity - etiology
Hyperesthesia or hypersensitivity of the teeth, is a condition characterized by a sharp pain or discomfort in the teeth. Appears hypersensitivity at different ages. In some - in adolescence, in some in 20-30 years and later. The prevalence of this symptom is as high as 62.3% (1) and is more common in women (2).
Many individuals experience sensitivity when their teeth are exposed to certain stimuli, such as:
- Thermal. Strong temperature changes, cold or hot foods, liquids, inhaled air.
- Chemical. Products with a pronounced flavor - sweet, or acidic foods and drinks.
- Mechanical. The touch of a toothbrush while cleaning the mouth.
The sensation can be brief but sharp and discomforting.
According to dentists, tooth sensitivity often occurs when the dentin, the softer, inner part of the tooth beneath the enamel, becomes exposed. This can happen due to enamel erosion, receding gums, or a damaged tooth. The exposed dentin has tiny channels, known as tubules, that lead to the tooth's nerve. Due to thinning enamel the dentinal tubules can become unprotected or wider. When these tubules are exposed to certain stimuli, it can trigger the nerve and cause pain.
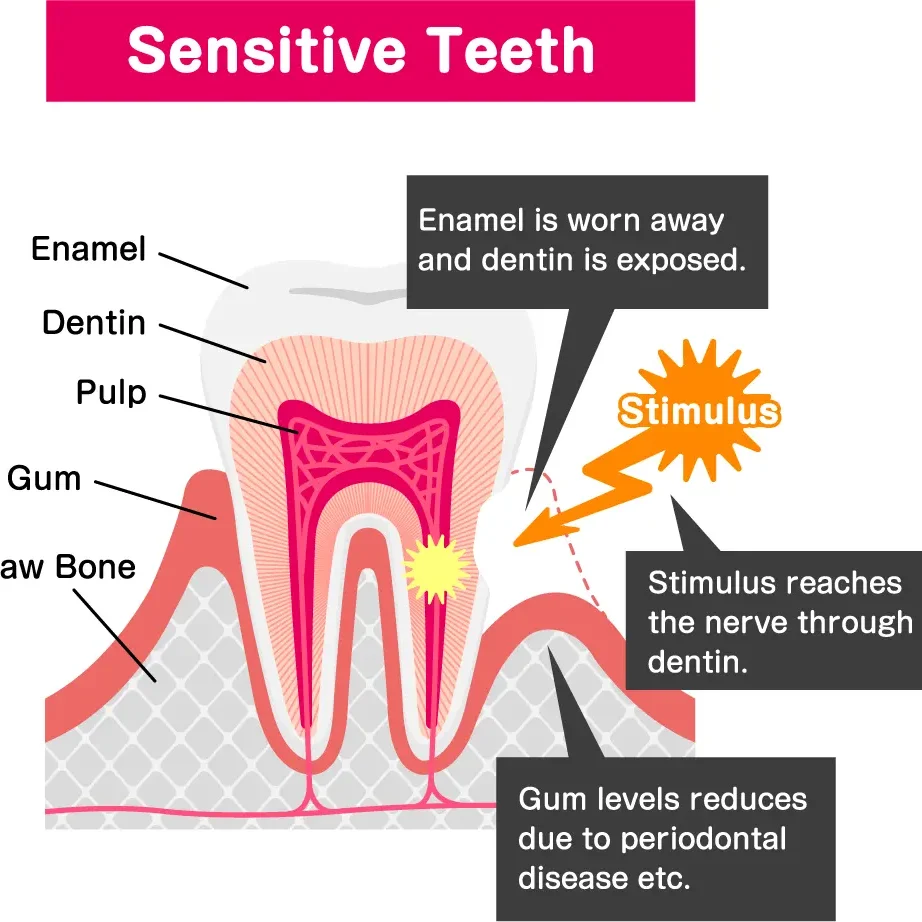
Hypersensitivity occurs in response to stimuli - temperature, chemical, or mechanical - and typically lasts only 10-30 seconds.
Regular tooth ache is more prolonged and aching. It arises from causes such as dental cavity, pulpitis, or other inflammations. Sometimes, it can lead to an increase in temperature or swelling.
Symptoms of Extreame Tooth Sensitivity
| Symptom | Manifestation |
|---|---|
| Sharp Pain | The pain appears for 10-30 seconds when interacting with a stimulus. For example, teeth may hurt outdoors due to cold air or when coming into contact with hot or cold food. The pain subsides after the stimulus is removed. |
| Wedge-shaped Defect | The gum edge recedes, exposing the tooth's neck. This affects the smile's aesthetics. This defect can be corrected with gum contouring surgery. |
| Enamel Thinning | The tooth surface in the cervical area is affected. The cutting edge and chewing surface also become thinned or completely worn away. |
These symptoms are not to be ignored, as they can be indicative of underlying dental issues. The pain is typically acute and quick in response to the triggering stimulus. If you experience these symptoms, a dentist can confirm if you indeed have hypersensitive teeth and identify the root cause, whether it's enamel erosion, exposed dentin, gum recession, or a fractured tooth. It's important to address these symptoms with a dental professional to prevent further dental health complications.
Tooth sensitivity - causes
Hyperesthesia comes in many different origins:
-
Caries
Infection from cavity affects dental tissues, exposing dentin tubules and nerve endings.
-
Periodontitis
Gum inflammation leads to deep periodontal pockets, exposing the tooth in the root area. This increases the impact of irritants on enamel and dentin.
-
Gum Recession
The gum edge recedes, exposing the enamel and creating a wedge-shaped defect. Bacteria and acids more aggressively affect dental tissues, causing damage.
-
Plaque Accumulation
Dental plaque and tartar contain aggressive bacteria that gradually destroy enamel.
-
Bruxism
Teeth grinding due to stress, malocclusion, or TMJ dysfunction leads to increased wear of dental tissues.
-
Malocclusion
Incorrect contact between upper and lower jaws also leads to increased wear of dental tissues.
-
Acidity Imbalance
Some gastrointestinal diseases or constant consumption of acidic foods increase saliva acidity, accelerating enamel erosion.
-
Smoking
Hot smoke and constant nicotine use cause dry mouth, reducing saliva's ability to wash away bacteria, increasing the risk of infection and dental tissue damage.
-
Mineral Deficiency
Loss of calcium, phosphorus, fluoride, and other elements makes enamel more fragile. This is often seen during pregnancy or vitamin deficiencies.
-
Hormonal Imbalance
Improper thyroid function and endocrine diseases also lead to enamel demineralization.
Due to tartar and plaque, dental tissues can become thinner and more fragile. After a professional cleaning, when the dentist removes all impurities, the enamel is exposed, making it more susceptible to external irritants.
Typically, a dental hygienist uses strengthening varnishes after professional cleaning. These varnishes reduce sensitivity, but a slight discomfort may persist for 2-3 days.
Types of hypersensitivity of teeth
There are two types of hypersensitivity based on prevalence:
- Localized. The pain affects only one tooth. The cause is usually isolated decay or gum edge recession.
- Generalized. The pain spreads to several adjacent teeth, and sometimes hypersensitivity affects the entire dental row. Causes can include multiple caries, enamel erosion, gum recession, or periodontitis.
Based on the severity, there are three stages of the pathology:
- Initial Stage. Pain occurs in response to high or low temperatures.
- Intermediate Stage. Pain intensifies not only due to temperature changes but also due to chemical irritants – salt, acid, sugar.
- Advanced Stage. Increased sensitivity exacerbates in response to high, low temperatures, chemical irritants, and also due to physical contact.

Doctor's Opinion
Boris Lipovetskiy
Dentist with 30 years of experience
How Can You Prevent Enamel Erosion?
Acid softens enamel, so it's better not to use a toothbrush or abrasive toothpaste for 1-2 hours after consuming acidic food. During this time, the enamel re-mineralizes from minerals present in saliva, becoming stronger.
However, the tooth surfaces still need prompt cleaning to prevent acids from damaging dental tissues. Therefore, instead of a brush and abrasive toothpaste, use dental floss or a mouthwash.
Diagnosis of Tooth Hypersensitivity
To determine the degree or cause of the pathology, we conduct a multi-stage diagnostic process:
The dentist assesses the condition of the enamel and gums, checking for increased wear of dental tissues and gum recession.
A stream of air at 20 degrees Celsius is directed onto the teeth. This helps the specialist determine how quickly pain appears in the patient and how long it takes to subside.
The dentist uses a periodontal probe to touch the tooth and surrounding areas. This test is necessary to assess the degree of hypersensitivity.
The dentist dries the enamel and isolates it from liquid. An electrode is attached and a low electric current is applied. The charge is gradually increased until the first pain reaction occurs. Depending on the pain threshold, the dentist determines the degree of hypersensitivity.
Tooth sensitivity - treatment
After diagnosis, the doctor accurately determines the cause of the pathology and then prescribes treatment to eliminate it:
- Filling for caries or pulpitis.
- Bite alignment for improper jaw closure.
- Treatment of periodontitis.
- Gum grafting for gum recession.
- Professional dental hygiene.
- Targeted treatment for non-dental related diseases.
Concurrently with addressing the cause of hypersensitivity, the doctor strengthens the dental tissues. There are several methods:
- Sealing the dentinal tubules, reducing fluid circulation speed and decreasing sensitivity. This is done using gels, varnishes, or remineralizing solutions.
- Reducing the sensitivity of nerve endings using products containing potassium nitrate.
- Narrowing the dentinal tubules with laser treatment. The laser fuses the liquor proteins and melts the hard tissues. The tubules become narrower, fluid circulation slows down, and nerve endings become less reactive to irritants. Research shows laser treatment yields the best results.
The doctor may employ multiple treatment methods to quickly alleviate pain and discomfort.
How Can You Reduce Tooth Sensitivity at Home?
Only a dentist can fully resolve the issue by identifying the exact cause of the pathology and prescribing appropriate treatment. This approach reduces the risk of hypersensitivity recurrence.
However, if the pain is severe and interferes with eating or drinking, you can alleviate it at home:
-
Use toothpaste for sensitive teeth
Products containing potassium nitrate (to affect nerve endings) can be helpful. Alternate these with pastes designed to seal dentinal tubules. Avoid using whitening products, and ensure the toothpaste's Relative Dentin Abrasivity (RDA) is below 100.
-
Replace your toothbrush with one having soft bristles
This will prevent further damage to the enamel and gums.
-
Adjust your die
Avoid highly acidic foods and drinks, such as juices, alcohol, and sodas.
-
Avoid smoking
This will help reduce dryness in the mouth and decrease pain sensations.
Yes, both an electric toothbrush and a water flosser can be used. However, it is important to be careful:
- The bristles of the electric toothbrush should be soft. Also, do not press the brush head too hard against the teeth to avoid damaging the enamel.
- The pressure of the water flosser should be minimal. If pain or discomfort occurs during cleaning, the water pressure should be reduced.
Dentin hypersensitivity - Complications
Constant tooth pain and lack of proper treatment can lead to serious consequences:
-
Gastrointestinal Diseases
As a reaction to usual foods, patients might change their diet. This can lead to stomach disorders, gastritis, ulcers, and cholecystitis.
-
Vitamin Deficiency
Also, due to dietary changes, the patient may not receive enough essential micronutrients. A lack of vitamins and minerals can lead to avitaminosis and potentially weaken the immune system.
-
Pulpitis
Constant irritation of nerve endings can lead to inflammation of the pulp, the nerve and vascular bundle inside the tooth. Pulpitis causes acute pain, fever, and is often accompanied by infection.
FAQ
No. The onset of hypersensitivity indicates an already advanced process of enamel destruction. The problem can only worsen over time. Therefore, it's important to see a dentist at the first signs of pain.
Sources of information


