Gum Disease Treatment
Are you experiencing bleeding, discomfort while chewing, or other signs of gum disease? Protect your smile from the hidden dangers of gum disease with our comprehensive periodontal care.
From early signs of gingivitis to advanced periodontitis, our expert dentists is equipped to halt the progression and restore your gum health. Embrace a proactive approach to your oral wellness. Schedule a consultation today to learn about our effective treatments for gum disease and reclaim the health of your gums and teeth.

What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease (periodontal disease) – is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. It is caused by the bacteria in plaque, a sticky, colorless film that constantly forms on teeth. If not adequately removed through brushing and flossing, plaque can build up and the bacteria can infect not only your gums and teeth but eventually the gum tissue and bone that support the teeth.
Types of periodontal disease:
- Gingivitis – the earliest stage, characterized by gum inflammation without bone loss. It's usually reversible with professional treatment and good oral home care.
- If gingivitis is not treated, it can advance to periodontitis. In this stage, gums pull away from the teeth and form pockets that are infected. The body’s immune response and bacterial toxins start to break down the bone and connective tissue. This stage requires more complex treatment.

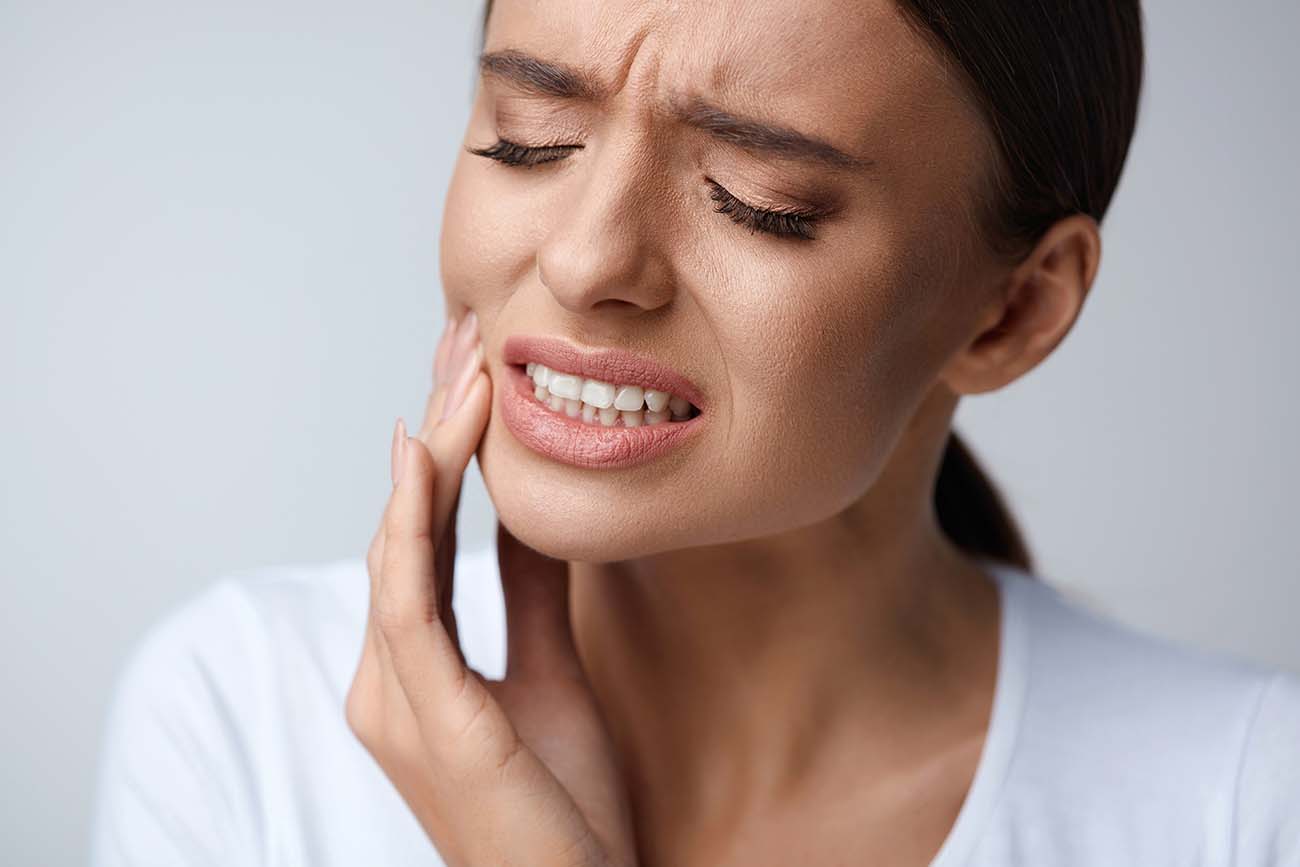
Symptoms of Gum Disease
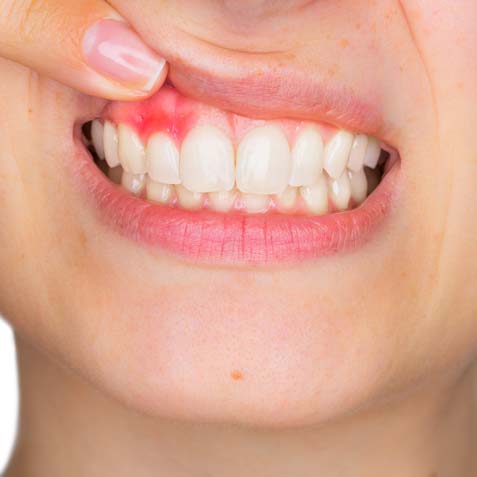
Gum disease can range from mild inflammation to serious damage to the soft tissue and bone. Common symptoms include:
-
Red, swollen, or tender gums.
-
Bleeding gums while brushing or flossing.
-
Receding gums, making teeth look longer.
-
Persistent halitosis or bad taste in the mouth.
-
Loose teeth or a change in the way teeth fit together.
-
Formation of deep pockets between teeth and gums.
Causes of Gum Disease
The primary cause of gum disease is the accumulation of plaque. However, other factors can contribute to periodontal disease:
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Nutrient deficiency.
- Crooked or curved teeth.
- Smoking or chewing tobacco.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Certain illnesses, such as diabetes, and their medications.
- Hormonal changes, such as those related to pregnancy.
- Substance abuse, obesity, and poor nutrition.
Treatment of Gum Disease
This procedure involves scraping off the tartar from above and below the gum line and smoothing rough spots on the tooth root.
Dentist can prescribe various medications to treat gum disease, including antibiotic gels, enzyme suppressants, and oral antibiotics.
In advanced cases, surgery might be required. Procedures can include flap surgery (pocket reduction surgery), soft tissue grafts, bone grafting, guided tissue regeneration.
It requires professional dental treatment, which may include deep cleaning (scaling and root planing), medications, and possibly surgery in severe cases.
It's important to recognize that while good oral hygiene can prevent many dental problems, including gum disease, once gum disease reaches a certain severity, professional intervention is essential to prevent further damage and potential tooth loss.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can gum disease be cured at home?
Gum disease, particularly in its early stage known as gingivitis, can often be managed and its progression halted with good oral hygiene practices at home. However, once it progresses to more advanced stages, such as periodontitis, professional dental treatment is necessary. Here's what you can do at home and when to seek professional help:
- Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Flossing helps to remove plaque and food particles between teeth and under the gumline.
- An antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce plaque and remove leftover food particles.
- Quit Smoking – smoke is a significant risk factor for the development and progression of gum disease.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: While these are not 'at home' measures, regular dental check-ups are crucial for maintaining gum health and catching problems early.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you notice persistent symptoms of gum disease such as red, swollen, bleeding gums, or bad breath that doesn't go away.
If the condition does not improve with good at-home care.In cases of advanced gum disease, professional cleaning and potentially more intensive treatments are necessary.